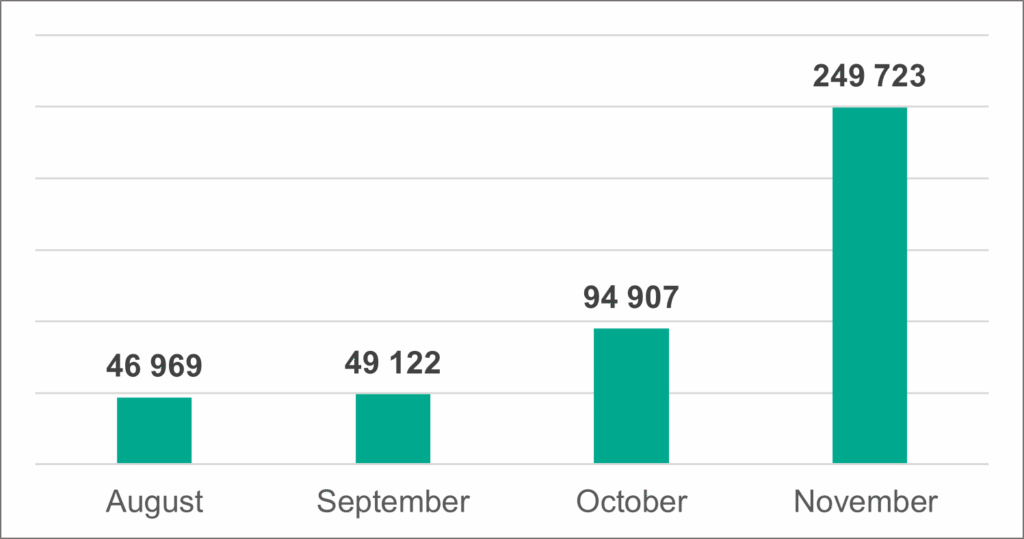
Cybercriminals are rapidly shifting toward QR Code Phishing as their preferred method for delivering malicious links. According to recent data from Kaspersky, the second half of 2025 saw an unprecedented spike in these attacks:
August 2025: 46,969 detections.
November 2025: 249,723 detections.
A staggering fivefold increase in just four months.
The surge is driven by the fact that QR codes are remarkably effective at bypassing legacy security layers. Unlike traditional URLs, which basic email filters can easily scan, QR codes act as a black box for many protective solutions.
- Attackers frequently hide QR codes within PDF attachments. This double-masking technique makes it harder for automated scanners to find the malicious link.
- Scanning a QR code typically shifts the victim from their protected work PC to a personal mobile device. Smartphones often lack the robust endpoint security found on corporate laptops, making them a soft target for credential theft.
- Creating a malicious QR code is nearly free, yet it provides a sophisticated way to hide malicious infrastructure from text-based detection.
Attackers are exploiting routine business communication to lower the victim’s guard. The most frequent lures identified in 2025 include:
- Fake login pages are designed to steal corporate credentials.
- Urgent requests for employees to sign vacation schedules or view termination lists.
- PDF invoices that include both a QR code and a phone number. If the user calls to cancel the fake charge, they are met by a live social engineer.
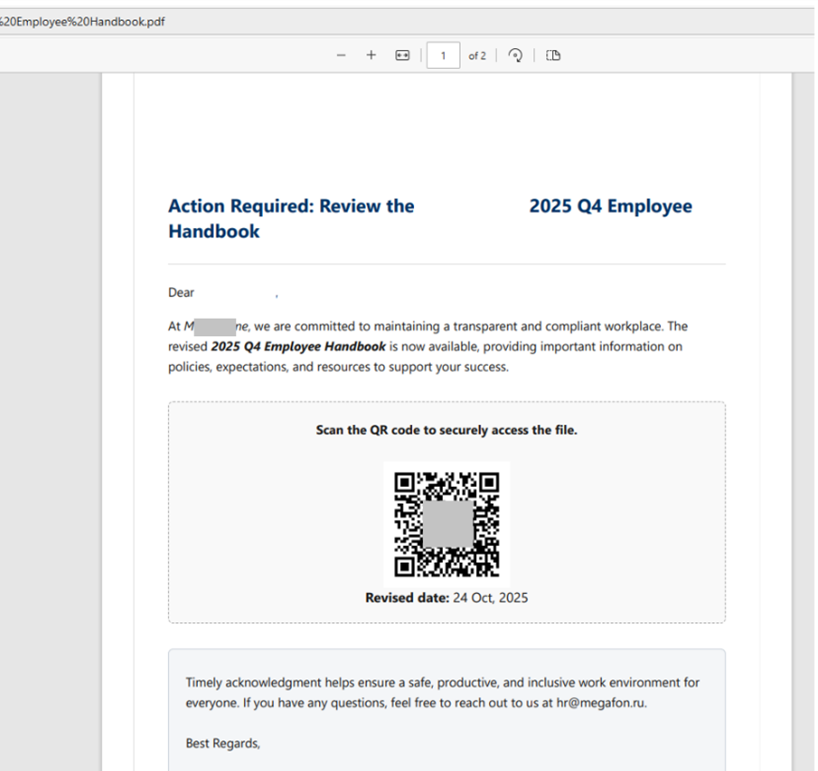
“Malicious QR codes have evolved into one of the most effective phishing tools, particularly when hidden in PDF attachments or disguised as legitimate business communications like HR updates. The explosive growth in November 2025 highlights how attackers are capitalizing on this low-cost evasion technique to target employees on mobile devices, where protection is often minimal.” — Roman Dedenok, Anti-Spam Expert at Kaspersky
Kaspersky recommends a two-pronged defense strategy to counter the rise of quishing in 2026:
- Advanced Gateway Protection: Deploying solutions like Kaspersky Security for Mail Server that use optical character recognition (OCR) and advanced image analysis to see and block malicious codes before they reach the inbox.
- Continuous Awareness Training: Educating employees to be skeptical of any QR code that arrives via unsolicited email, especially those hidden inside attachments or claiming to be from HR/Finance.